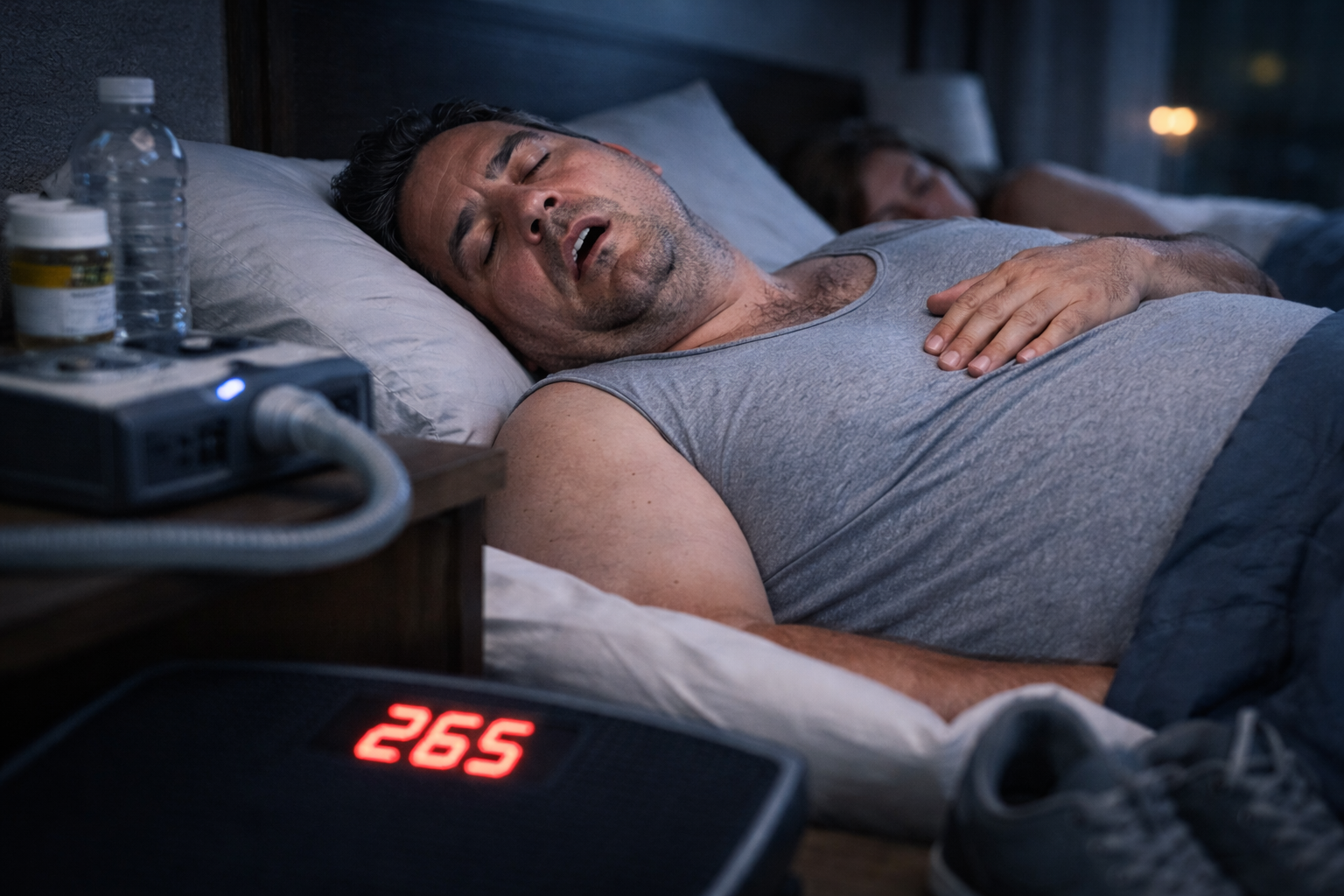
Weight fluctuations can influence far more than how you feel during the day—they can also have a profound impact on how you sleep at night. Even moderate changes in body weight can alter breathing patterns, disrupt sleep cycles, and increase the risk of nighttime disturbances that leave you feeling unrefreshed in the morning.
At El Paso Sleep Center, we help patients understand how physical changes in the body can affect nighttime rest and why persistent sleep issues should never be ignored. Recognizing the connection between weight and sleep is an important step toward better long-term health.
The Link Between Body Weight and Sleep Quality
Sleep is a complex biological process that depends on stable airflow, balanced hormones, and proper muscle tone. Changes in body weight can influence all three. When weight increases or decreases rapidly, the structures involved in breathing—such as the airway, neck, and chest wall—may be affected in ways that interfere with normal sleep.
These changes can contribute to a range of sleep disorders, especially those involving disrupted breathing. The impact is often gradual, which makes symptoms easy to overlook until sleep quality significantly declines.
How Weight Changes Influence Breathing at Night
Weight gain, particularly around the neck and upper body, can place additional pressure on the airway. During sleep, when muscles naturally relax, this pressure may increase the likelihood of airway narrowing or collapse.
This is why weight and sleep apnea are so closely connected. Even individuals who are otherwise healthy may begin to experience breathing irregularities when weight changes affect airway anatomy.
Common nighttime effects include:
- Reduced airflow during sleep
- Increased breathing effort
- Frequent micro-awakenings
- Drops in oxygen levels
These disruptions prevent the body from maintaining deep, restorative sleep stages.
Why Snoring Often Appears With Weight Gain
One of the earliest warning signs linked to physical changes is snoring. Weight gain and snoring often go hand in hand because added tissue around the throat can cause vibration as air moves through a narrowed airway.
Snoring may seem harmless, but it can indicate increasing resistance in airflow. Over time, this resistance may worsen and lead to more serious breathing disturbances during sleep.
Snoring associated with weight changes may:
- Become louder or more frequent
- Occur in new sleeping positions
- Be accompanied by choking or gasping sounds
- Lead to daytime fatigue
Ignoring these signs can delay diagnosis of more serious conditions.
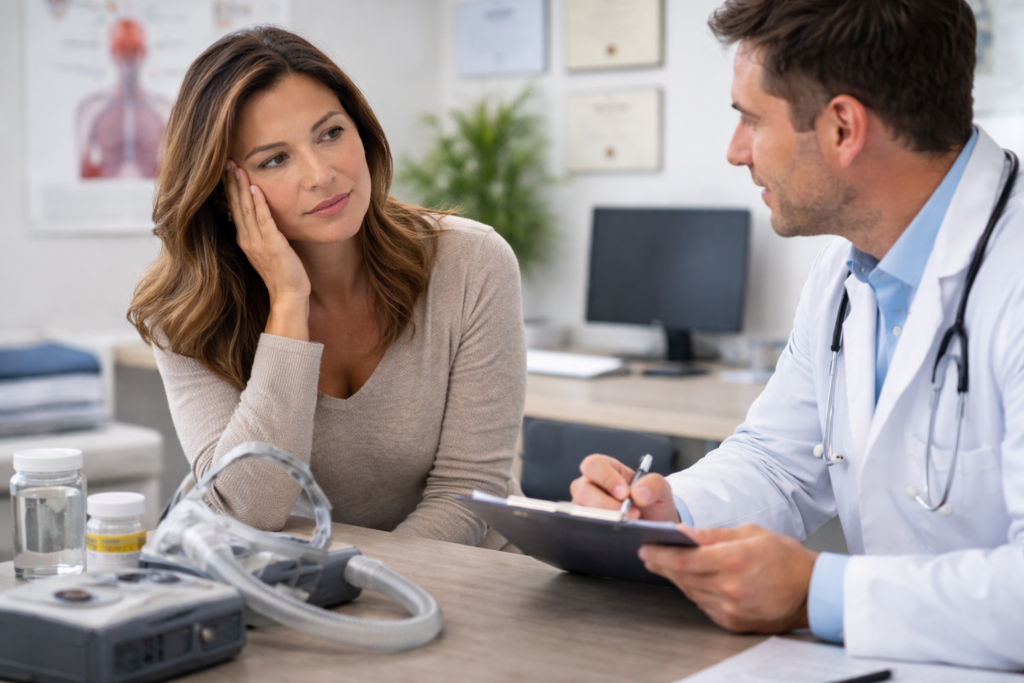

Weight Changes as a Risk Factor for Sleep Apnea
Body weight is one of several sleep apnea risk factors, but it is not the only one. Genetics, anatomy, age, and hormonal factors also play a role. However, changes in weight can amplify existing vulnerabilities and push the airway past a tipping point.
Even modest weight gain can worsen breathing instability during sleep, while significant weight loss—if unmanaged—can sometimes affect muscle tone or respiratory control. This is why sleep symptoms should be evaluated regardless of whether weight is increasing or decreasing.
The Broader Impact on Sleep Health
Disrupted breathing at night affects more than just rest—it influences overall sleep health and daytime functioning. When the body repeatedly shifts out of deep sleep to restore airflow, it triggers stress responses that can impact multiple systems.
Potential consequences include:
- Chronic fatigue and low energy
- Difficulty concentrating or remembering information
- Mood changes and irritability
- Increased cardiovascular strain
- Reduced resilience to stress
Over time, these effects can accumulate, making recovery more difficult without professional care.
Recognizing Breathing Issues During Sleep
Many people are unaware they experience breathing issues during sleep because disruptions often occur without full awakenings. Symptoms may only become apparent through indirect signs such as morning headaches, dry mouth, or persistent daytime sleepiness.
Partners may notice:
- Pauses in breathing
- Loud or irregular snoring
- Restless movements
- Sudden gasping or snorting sounds
For individuals who sleep alone, these clues may be missing, making clinical evaluation even more important.
When to Seek a Sleep Evaluation
If sleep quality declines after a change in weight—or if fatigue persists despite adequate sleep time—it may be time to seek professional assessment. A comprehensive sleep evaluation can determine whether breathing disruptions are occurring and how they are affecting sleep cycles.
At El Paso Sleep Center, diagnostic testing provides detailed insight into airflow, oxygen levels, and sleep stages. This information allows for personalized treatment plans that address both symptoms and underlying causes.
Treatment and Lifestyle Considerations
Managing sleep-related breathing issues often requires a multi-faceted approach. Treatment may include airway support therapies, oral appliances, positional strategies, or targeted lifestyle changes.
Effective management may involve:
- Addressing sleep posture and routines
- Treating nasal or airway obstructions
- Using prescribed sleep therapy devices
- Coordinating care with other healthcare providers
Early intervention can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce long-term health risks.
Conclusion
Weight changes can quietly but powerfully influence how you breathe and sleep at night. When sleep becomes fragmented or unrefreshing, it’s often a sign that something deeper is affecting your body’s ability to rest and recover. Understanding the connection between physical changes and sleep quality empowers individuals to seek answers sooner rather than later. With proper evaluation and care, restorative sleep is achievable—regardless of changes along the way.